Starting a plant-based diet is exciting and rewarding. But, you might wonder how to get enough protein. This guide is for you, whether you’re new to vegetarianism or veganism, or just want to eat more plant-based proteins. Learn about the essential role of protein, find the best plant-based protein sources, and learn how to plan your meals. You’ll get all the protein you need with our expert advice and tips.
Key Takeaways
- Plant-based diets can provide ample protein, often exceeding recommended daily intakes.
- Legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains are excellent sources of plant-based protein.
- Proper meal planning and combining various plant-based foods can ensure you get all the essential amino acids.
- Protein supplements, such as plant-based protein powders, can be a convenient addition to a plant-based diet.
- Athletes and individuals with higher protein needs can thrive on a well-planned plant-based diet.
Understanding Protein: The Building Blocks of Life
Protein is a key part of our diet. It’s made of 20 amino acids. Our bodies need eight of these amino acids, which we get from food. They help our cells grow, repair, and work right.
What Are Amino Acids and Why They Matter
Amino acids are the basic parts of proteins. They help our bodies in many ways. This includes building cells, making enzymes, and fighting off sickness.
- Building and repairing cells
- Creating enzymes and antibodies
- Transporting and storing nutrients
- Regulating hormones
- Providing energy
Essential vs Non-Essential Amino Acids
Amino acids are split into two groups: essential and non-essential. Essential amino acids are key and we get them from plant based diet protein. These are leucine, isoleucine, valine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, and histidine.
Non-essential amino acids are made by our bodies. They include alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine.
The Role of Protein in Body Functions
Protein is very important for our bodies. It helps with many things. This includes fixing tissues, making hormones, and helping our immune system.
- Tissue repair and maintenance
- Enzyme and hormone production
- Nutrient transportation
- Immune system support
- Energy production
It’s important to eat enough amino acids and protein functions. This helps us stay healthy. Knowing about protein helps us make good choices for our bodies.
“Protein is the building block of life, essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of our cells and tissues.”
Plant Based Diet Protein: Getting Started
Starting a plant-based diet is exciting and rewarding. It’s key to know about protein and how to get enough. Most people, even those who don’t eat meat, get more protein than they need.
The U.S. says you need 0.8 grams of protein for every kilogram of your weight. The World Health Organization says it’s 0.66 grams. For someone who weighs 140 pounds and eats 2,000 calories a day, they only need 50 grams of protein. That’s about 10% of their calories.
So, where can you find vegan protein sources and plant-based protein? Lentils and beans are great, with one cup of cooked lentils having 18 grams of protein. One cup of cooked beans has about 15 grams. Nuts, nut butters, edamame, and whole grains like quinoa and amaranth are also good meat-free protein choices.
“Focusing on significant changes, like replacing meat, milk, and eggs with whole plant-based foods, can make noticeable and measurable improvements in your health.”
When starting your plant-based diet, add about 1,000 calories of legumes, whole grains, and starchy vegetables to your day. This helps you get enough protein and enjoy the health benefits of a vegan protein diet.
Remember, changing to a plant-based diet takes time. With a bit of planning and trying new foods, you can find many tasty and healthy vegan protein sources. They will help power your body and keep you healthy.
Daily Protein Requirements on a Plant-Based Diet
Switching to a plant-based diet raises a big question: Can you get enough protein? The answer is yes. You can get all the protein you need on a plant based diet protein, even if you’re very active.
Calculating Your Personal Protein Needs
The general rule is to eat 10-15% of your daily calories as protein. This is true for everyone, even if you’re very active. To find out how much protein you need, multiply your weight in pounds by 0.36 to 0.86 (for athletes) or 0.8 (for regular adults). This will tell you how many grams of protein you should eat every day.
Common Myths About Protein Deficiency
Protein deficiency myths are everywhere, but they’re not true. Real protein deficiency is very rare. It mostly happens when people don’t eat enough calories. Eating a variety of plant-based foods can give you all the protein you need.
Optimal Protein Timing Throughout the Day
Eating protein at different times helps your body use it better. Try to eat 20-30 grams of protein at each meal. Also, have protein-rich snacks when you need them to meet your protein goals.
Knowing how much protein you need and eating a variety of plant-based foods can help you thrive on a plant-based diet.
Top Plant-Based Protein Sources for Beginners
Starting a plant-based diet doesn’t mean you lose protein. The plant world has many vegan protein sources that meet your needs. You’ll find great options like legumes and vegetables.
Legumes like beans, lentils, and chickpeas are full of protein. A half-cup of cooked lentils has almost 9 grams of plant-based protein. Chickpeas give about 7 grams per serving.
Soy-based foods like tofu, tempeh, and edamame are also great. They have 12-20 grams of vegan protein in every 3.5-ounce portion.
Whole grains like quinoa, teff, and spelt are full of protein and nutrients. A cooked cup of quinoa has about 8 grams of plant-based protein.
Nuts, seeds, and nut butters are also protein-rich. Peanuts or almonds give 16-20 grams of vegan protein. Chia and hemp seeds are also good for your diet.
Don’t forget about vegetables like broccoli, kale, and mushrooms. They add several grams of high-protein vegetables to your diet.
By using these vegan protein sources, you can meet your protein needs. You’ll also enjoy the health benefits of a plant-based lifestyle.
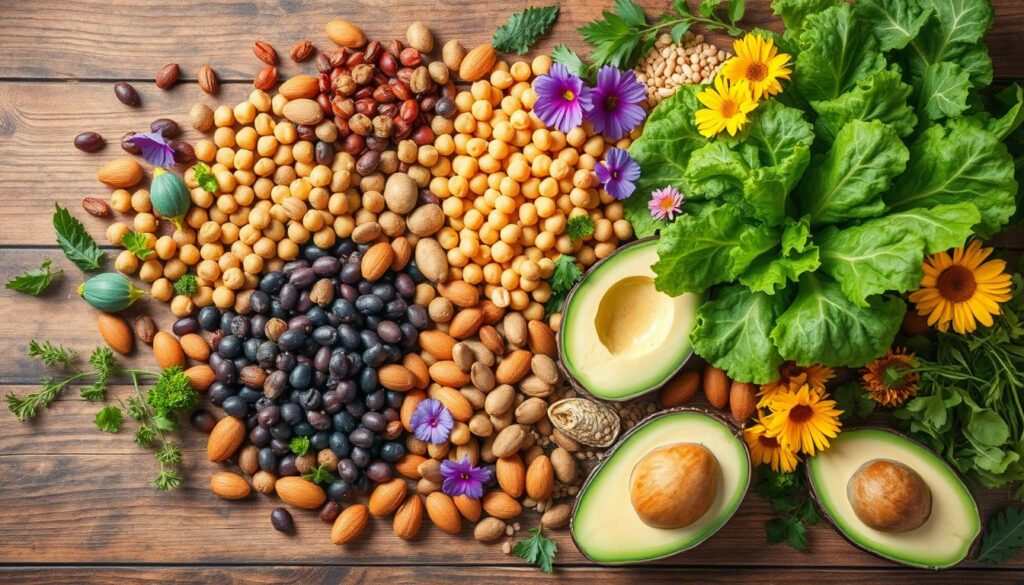

“A vegetarian or vegan diet can provide all the nutritional requirements of adults, children, and those who are pregnant or breast-feeding.”
– Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 2016
Legumes and Pulses: Your Protein Powerhouses
Legumes like beans, lentils, and peas are great for a plant-based diet. They are full of important nutrients. This makes them key for a healthy, balanced diet.
Best Beans for Protein Content
Some beans are better than others for protein. Tempeh, made from soy, has 34 grams of protein in 1 cup. Tofu and edamame also have lots of protein, with 20 and 18 grams in 1 cup, respectively.
Lentil Varieties and Their Benefits
Lentils are also great for protein. One cup of cooked lentils has 18 grams of protein. They come in many colors, each with its own benefits.
From brown lentils to red lentils and green lentils, they are affordable and versatile. They help you get more plant-based protein.
Preparing and Cooking Legumes
To get the most from legumes, prepare them right. Soaking beans and lentils before cooking makes them easier to digest. Trying different cooking methods can also help.
Adding different legumes and pulses to your plant-based diet helps meet your protein needs. Explore these ingredients and get creative in the kitchen.
| Food | Protein Content (per 1 cup) |
|---|---|
| Tempeh | 34 grams |
| Tofu | 20 grams |
| Edamame | 18 grams |
| Lentils (cooked) | 18 grams |
| Chickpeas (cooked) | 15 grams |
| Hemp Hearts (3 tbsp) | 10 grams |
| Soy Milk (1 cup) | 8 grams |
| Quinoa (cooked 1 cup) | 8 grams |
| Pistachios (1/4 cup) | 6 grams |
Nuts, Seeds, and Whole Grains as Protein Sources
Nuts, seeds, and whole grains are great for a plant-based diet. They give you protein and other good stuff like healthy fats and fiber.
Almonds have about 21% protein. Sunflower seeds have up to 21g of protein per 100g. Quinoa gives you about 8g of protein per cup.
Chia seeds have 4g of protein per ounce. Whole grains like oats have 6-8g of protein per cooked cup. Adding these to your meals helps meet your protein needs.
| Food | Protein Content |
|---|---|
| Almonds | 21% protein |
| Sunflower Seeds | 21g protein per 100g |
| Quinoa | 8g protein per cup |
| Chia Seeds | 4g protein per ounce |
| Whole Grains | 6-8g protein per cooked cup |
Adding these nuts and seeds protein and whole grain protein sources to your diet boosts your protein. It helps keep you healthy and strong.
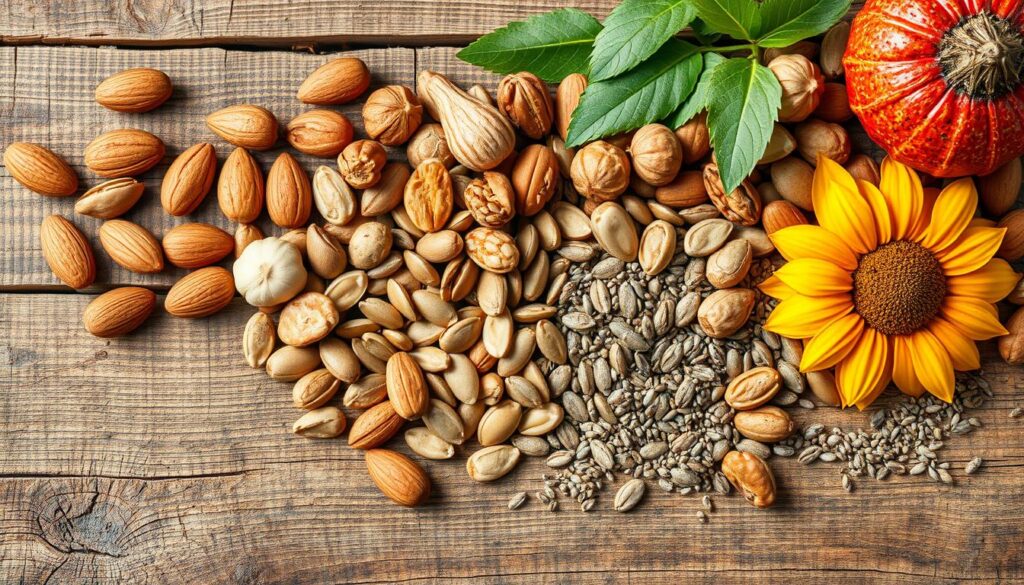

“Nuts, seeds, and whole grains are powerhouse protein sources that can transform your plant-based diet.”
Plant-Based Protein Powders and Supplements
Whole foods are the best for protein. But, plant-based protein powders and supplements can help too. They give you a lot of plant-based protein in one go.
Types of Vegan Protein Powders
There are many kinds of vegan protein powders. Here are a few:
- Pea protein
- Rice protein
- Hemp protein
- Soy protein
Each one has its own special mix of amino acids. Think about what you need and like when picking one.
How to Choose Quality Supplements
When picking a plant-based protein powder, look for these things:
- Protein Content: Find one with at least 20 grams of plant-based protein per scoop.
- Amino Acid Profile: Pick one with all the amino acids you need.
- Ingredient Quality: Go for organic, non-GMO, and no artificial stuff.
- Third-Party Testing: Make sure it’s been tested by others for safety and quality.
Choosing a good plant-based protein powder helps your health and fitness on a plant based diet.
Meal Planning for Optimal Protein Intake
Getting enough protein on a plant-based diet is easy. Good meal planning lets you mix different protein-rich foods all day. This way, your body gets all the amino acids it needs.
Try mixing different plant proteins in one meal. Beans or lentils with quinoa or brown rice is a great combo. Adding nuts, seeds, or nut butters also boosts protein and adds good fats, vitamins, and minerals.
Here are some easy high-protein meal ideas:
- Breakfast: Overnight oats with almond milk, chia seeds, and peanut butter
- Lunch: Lentil and vegetable curry over brown rice
- Snack: Edamame and roasted chickpeas
- Dinner: Tofu and veggie stir-fry with quinoa
| Nutrient | Daily Totals |
|---|---|
| Calories | 1,198 – 1,225 |
| Protein | 50 – 59 grams |
| Carbohydrates | 87 – 140 grams |
| Fiber | 30 – 36 grams |
| Fat | 55 – 81 grams |
| Saturated Fat | 7 – 25 grams |
| Sodium | 1,016 – 2,099 mg |
These meal plans show how to balance plant based diet protein, vegan meal planning, and high-protein vegetarian meals. Try new ingredients and mixes to find what you like. The most important thing is to have fun and eat well.
Athletes and High-Protein Plant-Based Diets
Many think plant-based athletes can’t do well in sports. But, they can do great. They might need a bit more nutrients, but not more protein. Athletes like Robert Cheeke and Rich Roll show a plant-based diet works well for them.
Pre and Post Workout Nutrition
Good food before and after working out is key for plant-based athletes. The American College of Sports Medicine says eat 5–10 grams of carbs for every kilogram of body weight. For protein, the International Society of Sports Nutrition suggests 1.2-2+ grams per kilogram of body weight, based on the sport and how hard you train.
Building Muscle on Plant Protein
Some think plant proteins can’t build muscle like animal proteins. But, studies show plant-based protein sources like soy powder work just as well. They improve strength and muscle size when protein content and training are the same.
Plant-based athletes can do well on a high-protein diet. They just need to eat a variety of vegan protein sources and plan their meals around workouts and rest.
“A Physicians Committee study found that plant-based athletes benefit from improvements in heart health, performance, and recovery.”
Common Challenges and Solutions
Plant-based diets are getting more popular. Vegans in America have grown by 500% from 2014 to 2017. It’s key to tackle the common issues with plant based diet protein intake. Many worry about the quality and completeness of vegan protein challenges.
But, a well-planned vegetarian protein foods diet can give you all the amino acids you need. By eating a variety of plant-based proteins like legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, you can get enough protein. You don’t need animal products for this.
- Educate yourself on the diverse range of plant based diet protein sources and their nutrient profiles.
- Learn proper food combining techniques to ensure you’re getting a complete amino acid profile.
- Experiment with new vegetarian protein foods and recipes to keep your meals interesting and nutritious.
Planning meals to get enough protein can be tough. Knowing your protein needs and meal timing helps. This way, you can meet your vegan protein challenges without upsetting your diet balance.
| Protein Source | Protein Content (per 100g) |
|---|---|
| Lentils | 25g |
| Tofu | 15g |
| Quinoa | 14g |
| Almonds | 21g |
| Chickpeas | 15g |
By tackling these common issues and finding solutions, you can keep your plant based diet protein intake high. This supports your health and well-being.
“The highest environmental impact of meat is associated with ruminants compared to grains, fruits, and vegetables.”
Conclusion
A plant-based diet can give your body all the protein it needs. You learn how much protein you need and find many plant protein sources. This way, you can enjoy the health benefits of eating plants.
Plant proteins are becoming more popular because they are healthier than animal proteins. People worry about the bad effects of eating too much animal protein. They are concerned about the high saturated fat intake.
With the right knowledge, you can get enough plant based diet protein. You can also learn the truth about vegan protein sources. This will help you live a healthy, healthy plant-based eating lifestyle. You’ll be on your way to better health and fitness with plant-based nutrition.

A Life-Changing Experience with This Weight Loss Supplement (Nagano Tonic)
I’ve always struggled with finding a weight loss solution that actually works for me. Like many, I’ve tried numerous diets, exercise routines, and supplements over the years—some worked for a short time, but nothing ever gave me long-term results. That was until I decided to try the weight loss supplement I found : Link to the Supplement.
From the moment I started using it, I noticed a difference. Not only did I feel more energized, but my cravings also became more manageable. The best part? I started seeing results much quicker than I anticipated! Over the course of just a few weeks, I noticed a significant reduction in belly fat and overall weight loss that I hadn’t been able to achieve before.
What makes this supplement stand out from all the others I’ve tried is how it supports me in my daily routine without any jitters or energy crashes. I’m able to stay focused and motivated, which has made it easier to stay on track with my diet and exercise plan.
This product truly exceeded my expectations, and I feel more confident and healthier than ever before. If you’re struggling with your weight loss journey like I was, I highly recommend giving this supplement a try. It’s been a game-changer for me, and I’m sure it can work wonders for you too!
Contant Them on email .. tonicnagano50@gmail.com
I’ve tried so many weight loss products over the years, but nothing worked like this supplement! Since I started using it, I’ve noticed a big difference in my energy levels and appetite control. In just a few weeks, I’ve lost weight and feel so much better. It’s been easy to stick with, and the results speak for themselves. Highly recommend this to anyone looking to make a real change!
I was skeptical at first, but this supplement has truly made a difference in my weight loss journey. I’ve lost weight without feeling deprived or sluggish. My cravings are under control, and I feel more confident in my body. It’s easy to incorporate into my daily routine, and the results speak for themselves. I’m so glad I gave it a try!
Thanks David, i do use the link to make my purchase. you can get too here http://surl.li/iasppy
wasn’t sure what to expect, but this weight loss supplement has really impressed me! After just a few weeks of use, I’ve already dropped a few pounds and feel more motivated to stay active. It’s helped curb my cravings and boosted my energy throughout the day. I’m excited to keep going and see even better results. Definitely worth trying!
Reach them on tonicnagano50@gmail.com
This Nagano Tonic has been amazing! In just a few weeks, I’ve lost weight, feel more energized, and my cravings are under control. Highly recommend it!
Thats the link to purchase http://surl.li/iasppy