Changing your low carb diet macros can really help you reach your health and fitness goals. You might want to lose weight, feel more energetic, or improve your metabolic health. This guide will cover the basics of low carb diets, the science behind carb restriction, and how to create a macro plan that fits you.
Low carb diets limit carbs to less than 26% of your daily calories. For a 2,000-calorie diet, that’s under 130 grams of carbs a day. High protein diets often give you more protein than you need. A standard ketogenic diet has 5-10% carbs, 55-60% fat, and 30-35% protein.
Key Takeaways
- Low carb diets restrict carb intake to less than 26% of total daily calories.
- High protein diets may provide more protein than the RDA of 0.8 g per kilogram of body weight.
- The typical ketogenic diet macros are 5-10% carbs, 55-60% fat, and 30-35% protein.
- Optimizing macros can support weight loss, improved energy, and better metabolic health.
- Understanding the principles of low carb dieting is essential for achieving your health and fitness goals.
Finding the right macronutrient balance is key to low carb diet success. By exploring the details in this guide, you’ll learn how to make a low carb macro plan that suits you. Let’s start your journey to better health and performance!
Discover how you can boostyour weight loss with a low carb.
Understanding Low Carb Diet Fundamentals
Starting a low carb diet means eating less carbs and more protein and healthy fats. This helps your body burn fat for energy instead of carbs. It also helps control blood sugar and can lead to weight loss and better health.
What Defines a Low Carb Diet
A low carb diet limits carbs to less than 100 grams a day. Some plans cut carbs even more, to 20-50 grams. This change helps your body use fat and ketones for energy, called metabolic flexibility.
The Science Behind Carb Restriction
Reducing carbs puts your body in ketosis, where it burns fat for energy. This not only aids in weight loss but also improves health. It boosts nutrient density, blood sugar control, and metabolic flexibility.
Key Principles of Macro Distribution
A low carb diet has about 5-10% carbs, 55-60% fats, and 30-35% protein. This balance helps your body get into ketosis and stay healthy. Eating more high-fat diet foods helps avoid bad carbs.
Benefits of Following Low Carb Diet Macros
Adding a low carb diet to your life can bring many benefits. One big plus is weight loss. Studies show low carb diets can lead to quick weight loss, especially in the first 6 to 12 months. This is because they help burn more calories than high-carb diets.
Low carb diets also improve body shape, blood sugar control, and brain function. They often include more protein. This can make you feel full, reduce hunger, and speed up your metabolism. All these help with weight loss.
Research also shows low carb diets might lower the risk of bone loss and fractures in older people. They can also lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels. But, more research is needed to fully understand these benefits.
“The ketogenic diet typically reduces total carbohydrate intake to less than 50 grams a day, and can be as low as 20 grams a day.”
It’s key to remember that everyone reacts differently to low carb diets. They can be hard to stick to because they are high in fat. Always talk to a doctor before making big changes to your diet.
Different Types of Low Carb Diet Approaches
There are many low carb diets to choose from. Each one fits different lifestyles and goals. Knowing the differences helps you pick the best one for you.
Standard Ketogenic Diet (SKD)
The standard ketogenic diet (SKD) is very popular. It limits carbs to 10% of your calories. Fats make up 70%, and proteins are 20%.
This mix helps your body burn fat instead of sugar. It’s called ketosis.
Targeted Ketogenic Diet (TKD)
The targeted ketogenic diet (TKD) lets you eat more carbs before working out. You get 10-15% carbs, 65-70% fats, and 20% proteins.
This extra carb helps give you quick energy for workouts. It keeps you in ketosis.
High-Protein Ketogenic Diet
The high-protein ketogenic diet (HPKD) focuses on more protein. It has 5% carbs, 60% fats, and 35% proteins.
This diet helps keep muscle mass and supports athletes. It’s good for those in ketosis.
Every low carb diet has its own benefits. They meet different needs. Knowing about them helps you choose the right one for your goals.
Calculating Your Personal Macro Needs
Finding the right macronutrient ratios is key for your low carb diet. Your needs depend on age, sex, activity level, and weight loss goals.
Active people should eat at least 100g of carbs daily. This helps with fiber and nutrients. Protein needs vary from 1.2 to 2 grams per kilogram of body weight, based on activity.
To figure out fat intake, adjust it for calorie needs and low carb ratio. A good rule is to get 80% of calories from healthy fats, 15-20% from protein, and less than 5% from carbs.
Online keto calculators can find your macro needs. They use formulas like the Mifflin-St. Jeor Equation. This helps estimate your basal metabolic rate (BMR) and total daily energy expenditure (TDEE).
| Macronutrient | Recommended Intake |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 5% or less of total calories (average 20g net carbs per day) |
| Protein | 0.8-1.0g per pound of lean body mass for active individuals |
| Fat | 80% of total caloric intake |
Your macro needs can change. It’s important to try different ratios and see how your body reacts. Using a macro tracking app or online tool can help you stay on track with your low carb diet.
“Tailoring your macros to your individual needs is key to achieving successful results on a low carb diet.”
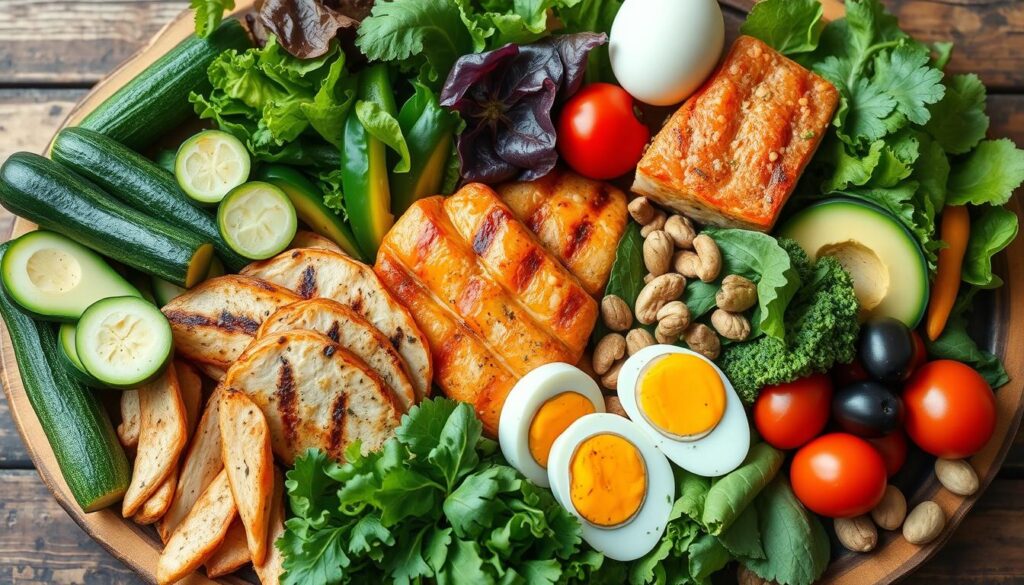
Essential Foods for Low Carb Success
Starting a low-carb diet means choosing foods wisely. Focus on lean proteins, healthy fats, and low-carb veggies and fruits. Let’s look at key foods for low-carb success.
Protein Sources to Prioritize
On a low-carb diet, eat lean protein sources to keep muscles strong. Good choices are eggs, chicken, beef, and fatty fish like salmon. Tofu and edamame are great plant-based options too.
Healthy Fat Options
Healthy fats are key in a low-carb diet. Enjoy avocados, olive oil, nuts, and seeds. They help you feel full and keep you healthy.
Low Carb Vegetables and Fruits
Even on a low-carb diet, you can eat some carbs. Choose non-starchy veggies like broccoli and leafy greens. Berries are good fruits to eat in small amounts.
“A low-carb lifestyle doesn’t mean missing out on tasty foods. Focus on lean protein sources, healthy fats, and low-carb vegetables and fruits. This way, you get a balanced diet that’s good for your health and weight loss.”
Foods to Avoid on a Low Carb Diet
Starting a low carb diet means watching what you eat closely. It’s important to know which foods to cut down on or avoid. Choosing foods rich in nutrients helps keep your diet balanced, even when you’re watching carbs.
Grains are a big no-no on a low carb diet. This includes bread, rice, pasta, and baked goods. They’re full of carbs. Also, eat starchy veggies like potatoes, corn, and legumes only in small amounts.
Sweeteners, both natural and fake, are off-limits. This includes sugar, honey, maple syrup, agave, and artificial sweeteners. Sugary drinks like soda, juice, and some sports drinks need to go too. Instead, drink water, unsweetened tea, or low-carb drinks.
Processed foods high in carbs, like chips, fries, and pizza, should be cut down or out. These foods have lots of carbs and often lack the nutrients your body needs.
Stick to foods low in carbs but rich in nutrients. Choose lean proteins, healthy fats, and veggies that aren’t starchy. This way, you can follow a low carb diet that’s good for your health and meets your goals.
| Food Group | Carb Content | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Grains (bread, rice, pasta, baked goods) | High | Limit or avoid |
| Starchy Vegetables (potatoes, corn, legumes) | Moderate to High | Consume in moderation |
| Sweeteners (sugar, honey, maple syrup, agave) | High | Limit or avoid |
| Sugary Drinks (sodas, juices, sports drinks) | High | Avoid |
| Processed, High-Carb Foods (chips, fries, pizza) | High | Limit or avoid |
A successful low carb diet isn’t about missing out. It’s about finding nutrient-dense foods that fit your carb counting and health goals.

Meal Planning and Macro Tracking Tips
Planning your meals well is key when you’re on a low carb diet. Using apps to track macros helps you keep an eye on carbs, proteins, and fats. These apps give you detailed info to help you meet your goals.
Using Macro Tracking Apps
Apps like MyFitnessPal, Cronometer, and Lose It! make tracking food easy. They have big food databases and even let you scan barcodes. Using these apps helps you make smart food choices.
Meal Prep Strategies
Meal prep is a big help for a low carb diet. Spend time on weekends or a special day to cook proteins like chicken or eggs. Also, prep veggies like broccoli and greens ahead of time. This way, you always have healthy, low carb meals ready.
Portion Control Guidelines
It’s important to control your portions for the right balance. Use cups, spoons, or visual guides to know the right sizes. For example, a protein serving is as big as your palm. Healthy fats are as big as your thumb. Low carb veggies should fill half your plate. This helps you not eat too much and stay on track.
Using apps, meal prepping, and portion control can make your low carb diet easier. Remember, being consistent and mindful is important for good macronutrient balance.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Starting a low-carb diet can be exciting but also tough. One big challenge is the “keto flu.” It makes you feel tired, have headaches, and feel sick. This happens when your body starts using fat instead of sugar for energy.
But, you can make these symptoms better. Drink lots of water and eat foods that are full of good stuff like sodium, potassium, and magnesium. Eating foods that are low in carbs but full of nutrients can also help.
It’s also hard to stop wanting foods that are full of carbs. Eating foods that are high in healthy fats and fiber can help. These foods make you feel full and keep your blood sugar steady. Using portion control and planning your meals can also help when you’re out eating.

Every person is different when it comes to low-carb diets. What works for one person might not work for another. Be patient, flexible, and open to trying new things. This will help you find what works best for your body and health.
Exercise and Low Carb Diet Macros
Starting a low carb diet doesn’t mean you must stop exercising. Exercise can help your body stay healthy and flexible. But, you might need to change how you eat before and after working out.
Pre-Workout Nutrition
Your body gets used to using fat for energy on a low carb diet. But, for hard workouts, a little bit of easy-to-digest carbohydrates can help. Try eating a piece of fruit or some berries about 30 minutes before you exercise.
Post-Workout Recovery
After working out, eat enough lean protein sources to fix your muscles. Good choices are whey protein, eggs, or grilled chicken. Add healthy fats like avocado or nuts to make a good meal.
Performance Considerations
Starting a low carb diet might make you feel less strong at first. But, your body will get better at using fat for energy. Soon, you’ll feel stronger and last longer during workouts.
Everyone’s body is different. So, be kind to yourself and listen to what your body needs. By adjusting your eating before and after workouts, you can keep enjoying your diet and exercise.
Conclusion
Low-carb diets can help with weight loss and better health. They are good for controlling blood sugar and heart health. It’s key to know about carbs, nutrients, and the keto diet.
Early studies look good, but we need more on long-term effects. How well you stick to these diets matters a lot. This affects how well they work.
What’s best for you depends on your needs and likes. Always talk to a doctor before changing your diet. This way, you can make a plan that fits your health goals.

A Life-Changing Experience with This Weight Loss Supplement (Nagano Tonic)
I’ve always struggled with finding a weight loss solution that actually works for me. Like many, I’ve tried numerous diets, exercise routines, and supplements over the years—some worked for a short time, but nothing ever gave me long-term results. That was until I decided to try the weight loss supplement I found : Link to the Supplement.
From the moment I started using it, I noticed a difference. Not only did I feel more energized, but my cravings also became more manageable. The best part? I started seeing results much quicker than I anticipated! Over the course of just a few weeks, I noticed a significant reduction in belly fat and overall weight loss that I hadn’t been able to achieve before.
What makes this supplement stand out from all the others I’ve tried is how it supports me in my daily routine without any jitters or energy crashes. I’m able to stay focused and motivated, which has made it easier to stay on track with my diet and exercise plan.
This product truly exceeded my expectations, and I feel more confident and healthier than ever before. If you’re struggling with your weight loss journey like I was, I highly recommend giving this supplement a try. It’s been a game-changer for me, and I’m sure it can work wonders for you too!
Contant Them on email .. tonicnagano50@gmail.com
I’ve tried so many weight loss products over the years, but nothing worked like this supplement! Since I started using it, I’ve noticed a big difference in my energy levels and appetite control. In just a few weeks, I’ve lost weight and feel so much better. It’s been easy to stick with, and the results speak for themselves. Highly recommend this to anyone looking to make a real change!
wasn’t sure what to expect, but this weight loss supplement has really impressed me! After just a few weeks of use, I’ve already dropped a few pounds and feel more motivated to stay active. It’s helped curb my cravings and boosted my energy throughout the day. I’m excited to keep going and see even better results. Definitely worth trying!
Reach them on tonicnagano50@gmail.com
I was skeptical at first, but this supplement has truly made a difference in my weight loss journey. I’ve lost weight without feeling deprived or sluggish. My cravings are under control, and I feel more confident in my body. It’s easy to incorporate into my daily routine, and the results speak for themselves. I’m so glad I gave it a try!
Thanks David, i do use the link to make my purchase. you can get too here http://surl.li/iasppy
I’ve tried so many weight loss products, but this one has been by far the most effective. In just a few weeks, I’ve noticed a visible difference in my body and energy levels. It’s helped me stay on track without the constant hunger pangs and cravings. I’m really happy with my progress and can’t wait to see where I’ll be in another month!
This Nagano Tonic has been amazing! In just a few weeks, I’ve lost weight, feel more energized, and my cravings are under control. Highly recommend it!
Thats the link to purchase http://surl.li/iasppy