Are you looking for a way to lose weight or improve your health? You might think about a low-carb or ketogenic (keto) diet. Both diets cut down on carbs, but they’re different in how much and how they affect your body. Knowing the differences can help you choose the right diet for you.
This article will tell you about the main differences between low-carb and keto diets. We’ll also look at their health benefits and challenges. By the end, you’ll know which diet might be best for you.
Key Takeaways
- Low-carb diets usually let you eat 50-150 grams of carbs a day. Keto diets limit carbs to under 50 grams.
- Keto diets want 70-80% of your calories to come from fats, 15-30% from proteins, and 5-10% from carbs.
- Low-carb diets are easier to stick with for a long time. But they might not help you lose weight as fast as keto.
- Keto diets can make your heart healthier and help with type 2 diabetes and epilepsy.
- Both diets need careful planning to get enough nutrients and avoid side effects.
Understanding Low Carb vs Keto: Key Differences
Low-carb and ketogenic diets are different. They both cut down on carbs. But, they have different rules for how much to eat.
Defining Carb Restrictions
A low-carb diet lets you eat 50-150 grams of carbs a day. This is 10-30% of your daily calories. The ketogenic diet is stricter. It limits carbs to under 50 grams a day, or 5-10% of your calories.
Macronutrient Distribution
The ketogenic diet has more fat. It gets 70-80% of its calories from fat. It also has 15-30% from protein and 5-10% from carbs.
A low-carb diet has more protein and fat. It can get up to 50% of its calories from protein.
Daily Caloric Composition
The ketogenic diet limits carbs to start ketosis. This is when your body uses fat for energy instead of carbs. This is the main difference between the diets.
What is a Low Carb Diet: Basic Principles
A low carb diet limits carbs from grains, sugary drinks, and bread. It focuses on protein, healthy fats, and vegetables. This diet aims to cut calories and lose weight by avoiding high-carb foods.
Research shows low carb diets help with blood sugar control and lower cardiovascular risk factors. For someone eating 2,000 calories a day, it means 50-150 grams of carbs.
The ketogenic diet is stricter, with less than 50 grams of carbs daily. It tries to make the body use fat as its primary fuel source. While it can help with weight loss, it’s harder to follow long-term than a low carb diet.
“A low carb diet may result in weight loss and improved blood sugar control, particularly beneficial for people with diabetes.”
The Ketogenic Diet Explained
The ketogenic diet is a great way to change how your body uses energy. It makes your body use fat and ketones instead of carbs. This diet can help you feel better in many ways.
Understanding Ketosis
Ketosis is when your body burns fat for energy instead of carbs. By eating very few carbs, your body starts making ketones. This is good for your health.
Fat Adaptation Process
Getting used to the ketogenic diet takes time. It can take days to weeks. Your body learns to use fat and ketones for energy. You might feel more energetic and focused.
Required Macronutrient Ratios
- Carbohydrates: Less than 50 grams a day, or 5-10% of calories
- Protein: About 20% of total calories
- Fats: Around 70% of total calories, choose healthy fats
Keeping the right balance of nutrients is key. It helps your body burn fat and get the diet’s benefits.
Low Carb Diet vs Keto: Main Distinctions
Low carb and keto diets are different in carbs, protein, and fat. They both cut down on carbs but in different ways.
Low carb diets let you eat 50-150 grams of carbs daily. This is 10-25% of your calories. Keto diets are stricter, with less than 50 grams of carbs daily. This is only 5-10% of your calories.
Protein intake varies too. Low carb diets might have 40-50% of calories from protein. Keto diets aim for 20% of calories from protein. This helps keep you in ketosis.
Fat intake is the biggest difference. Low carb diets get 30-40% of calories from fat. Keto diets need 70-80% of calories from fat. This is what puts you in ketosis.
Keto diets are stricter and might be hard to follow long-term. But, both diets can help with weight loss and better health.
| Metric | Low Carb Diet | Ketogenic Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Carb Intake | 50-150 grams per day (10-25% of total calories) | Under 50 grams per day (5-10% of total calories) |
| Protein Intake | 40-50% of total calories | Around 20% of total calories |
| Fat Intake | 30-40% of total calories | At least 70-80% of total calories |
The main difference is how much carbs, protein, and fat you eat. Knowing this helps choose the right diet for you.

Health Benefits and Weight Loss Potential
Low-carb and ketogenic diets can help a lot with health and weight loss. They make your body better at using insulin and can lower cholesterol and triglycerides. The ketogenic diet is especially good for managing epilepsy and may help with other health issues too.
Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
These diets cut down on carbs a lot. This helps lower blood sugar and insulin levels. It can even help people with type 2 diabetes manage their condition better.
Effects on Body Composition
Low-carb and ketogenic diets are better for losing weight than low-fat diets. How much carbs you cut down affects how much weight you lose. These diets help you lose fat but keep your muscle mass.
Metabolic Changes
These diets change how your body uses energy. They make your body use fat and ketones instead of sugar. This can improve your cholesterol, reduce inflammation, and even help your brain work better. But, it’s important to watch out for nutrient deficiencies over time.
| Metric | Low-Carb Diet | Ketogenic Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrate Intake | 20-100 grams per day | 0-25 grams per day |
| Fat Intake | 10-30% of total calories | 75-85% of total calories |
| Protein Intake | 10-30% of total calories | 15-25% of total calories |
| Weight Loss Potential | Moderate to high | High |
| Impact on Blood Sugar | Significant reduction | Significant reduction |
| Effects on Body Composition | Favors fat loss, preserves lean muscle | Favors fat loss, preserves lean muscle |
| Metabolic Changes | Improved lipid profile, reduced inflammation | Improved lipid profile, reduced inflammation, enhanced cognitive function |
In summary, both low-carb and ketogenic diets can help a lot with health and weight loss. The amount of carbs you cut down affects how much you lose. The ketogenic diet might offer extra benefits, but watch out for nutrient deficiencies.
Potential Side Effects and Challenges
Starting a low-carb or ketogenic diet can have side effects and challenges. You might feel weakness, constipation, and nutrient deficiencies at first. The keto diet can also cause “keto flu,” with headaches, fatigue, brain fog, and irritability.
Sticking to these diets for a long time can be hard. The keto diet is stricter than a low-carb diet. You might find it hard to lose weight again after stopping the keto diet.
- Dehydration and stomach problems like constipation, diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting are common early side effects.
- You might not get enough vitamins and minerals because you eat fewer fruits and vegetables.
- Athletes might do worse on high-intensity tasks when first starting the keto diet.
Think carefully about the good and bad sides of low-carb or keto diets. Talking to a healthcare professional can help. They can guide you to a diet that works for you.

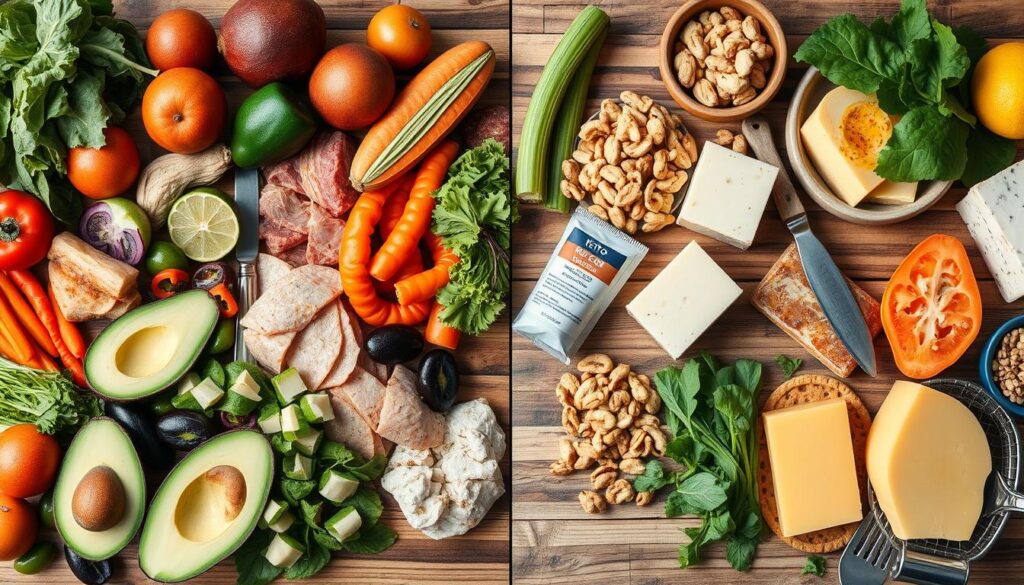
Food Choices and Meal Planning
Following a low-carb or ketogenic diet means eating foods that are full of nutrients. These foods help you feel full and give you energy. You need to eat healthy fats, protein, and low-carb vegetables to stay healthy and manage your weight.
Approved Foods List
For a low-carb diet, eat foods like:
- Meat, poultry, and seafood
- Eggs
- Nuts and seeds
- Avocados, olives, and other healthy fats
- Low-carb vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, and cauliflower
- Some berries and citrus fruits
The ketogenic diet is similar but focuses more on healthy fats. It also limits carbs to help your body use fat for energy. Foods you can eat include:
- Fatty cuts of meat, fish, and poultry
- Eggs
- Cheese, heavy cream, and other high-fat dairy
- Nuts, seeds, and nut butters
- Avocados, olives, and coconut oil
- Low-carb vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, and zucchini
Sample Meal Plans
Good meal planning is key for both diets. Here are some meal ideas to start with:
Low-Carb Meals:
- Breakfast: Spinach and feta scrambled eggs with avocado
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, tomatoes, and balsamic vinaigrette
- Dinner: Baked salmon with roasted Brussels sprouts and cauliflower
Keto Meals:
- Breakfast: Bacon and egg muffins with cheddar cheese
- Lunch: Bunless cheeseburger with a side of sautéed zucchini
- Dinner: Creamy garlic shrimp over zucchini noodles
By choosing foods that are nutrient dense and full of healthy fats, you can succeed on either diet. Good meal planning is the secret to success.
Who Should Choose Which Diet
Choosing between a low-carb diet and a ketogenic (keto) diet depends on your health, lifestyle, and weight loss goals. Each diet has its own benefits. Your personal needs and preferences should decide which one is right for you.
A low-carb diet is good for slow, steady weight loss and better health. It lets you eat 50-150 grams of carbs daily. This diet has 10-25% carbs, 40-50% protein, and 30-40% fat. It’s easier to stick to for a long time.
For quick weight loss or health benefits, consider a keto diet. It limits carbs to 5-10% of calories. You eat more healthy fats (70-80%) and some protein (15-20%). This can help with weight loss and health issues.
But, a keto diet might not be safe for everyone. It’s not good for pregnant or lactating women, people with kidney or gallbladder problems, or those at risk for heart disease. For them, a low-carb diet might be safer and more lasting.
Talking to a healthcare provider is important. They can help pick the best diet for you. Remember, sticking to your diet for a long time is key to reaching your goals.
Conclusion
Low-carb and ketogenic diets can help you reach your health goals. The best choice depends on your needs and what you like. It also depends on how well you can stick to it.
Low-carb diets are more flexible. They let you slowly cut down on carbs while eating a variety of foods. This might make it easier to stick with it for a long time.
The ketogenic diet is stricter. You have to cut carbs a lot to get into ketosis. It can help you lose weight fast, but it’s harder to keep up.
The best diet is one you can really do. It should help you stay healthy and feel good. Talk to a doctor or dietitian to find the right diet for you.

A Life-Changing Experience with This Weight Loss Supplement (Nagano Tonic)
I’ve always struggled with finding a weight loss solution that actually works for me. Like many, I’ve tried numerous diets, exercise routines, and supplements over the years—some worked for a short time, but nothing ever gave me long-term results. That was until I decided to try the weight loss supplement I found : Link to the Supplement.
From the moment I started using it, I noticed a difference. Not only did I feel more energized, but my cravings also became more manageable. The best part? I started seeing results much quicker than I anticipated! Over the course of just a few weeks, I noticed a significant reduction in belly fat and overall weight loss that I hadn’t been able to achieve before.
What makes this supplement stand out from all the others I’ve tried is how it supports me in my daily routine without any jitters or energy crashes. I’m able to stay focused and motivated, which has made it easier to stay on track with my diet and exercise plan.
This product truly exceeded my expectations, and I feel more confident and healthier than ever before. If you’re struggling with your weight loss journey like I was, I highly recommend giving this supplement a try. It’s been a game-changer for me, and I’m sure it can work wonders for you too!
Contant Them on email .. tonicnagano50@gmail.com
I’ve tried so many weight loss products over the years, but nothing worked like this supplement! Since I started using it, I’ve noticed a big difference in my energy levels and appetite control. In just a few weeks, I’ve lost weight and feel so much better. It’s been easy to stick with, and the results speak for themselves. Highly recommend this to anyone looking to make a real change!
wasn’t sure what to expect, but this weight loss supplement has really impressed me! After just a few weeks of use, I’ve already dropped a few pounds and feel more motivated to stay active. It’s helped curb my cravings and boosted my energy throughout the day. I’m excited to keep going and see even better results. Definitely worth trying!
Reach them on tonicnagano50@gmail.com
I was skeptical at first, but this supplement has truly made a difference in my weight loss journey. I’ve lost weight without feeling deprived or sluggish. My cravings are under control, and I feel more confident in my body. It’s easy to incorporate into my daily routine, and the results speak for themselves. I’m so glad I gave it a try!
Thanks David, i do use the link to make my purchase. you can get too here http://surl.li/iasppy
I’ve tried so many weight loss products, but this one has been by far the most effective. In just a few weeks, I’ve noticed a visible difference in my body and energy levels. It’s helped me stay on track without the constant hunger pangs and cravings. I’m really happy with my progress and can’t wait to see where I’ll be in another month!
This Nagano Tonic has been amazing! In just a few weeks, I’ve lost weight, feel more energized, and my cravings are under control. Highly recommend it!
Thats the link to purchase http://surl.li/iasppy